Knowledge Of The Farthest Known Object In The Solar System Will "Expand Exponentially" With Flyby
NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft is three months from returning to humanity the first-ever close up images and scientific observations of distant Pluto and its system of large and small moons.
"Scientific literature is filled with papers on the characteristics of Pluto and its moons from ground based and Earth orbiting space observations, but we’ve never studied Pluto up close and personal,” said John Grunsfeld, astronaut, and associate administrator of the NASA Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters in Washington. “In an unprecedented flyby this July, our knowledge of what the Pluto systems is really like will expand exponentially and I have no doubt there will be exciting discoveries."
The fastest spacecraft ever launched, New Horizons has traveled a longer time and farther away – more than nine years and three billion miles – than any space mission in history to reach its primary target. Its flyby of Pluto and its system of at least five moons on July 14 will complete the initial reconnaissance of the classical solar system. This mission also opens the door to an entirely new “third” zone of mysterious small planets and planetary building blocks in the Kuiper Belt, a large area with numerous objects beyond Neptune’s orbit.
The flyby caps a five-decade-long era of reconnaissance that began with Venus and Mars in the early 1960s, and continued through first looks at Mercury, Jupiter and Saturn in the 1970s and Uranus and Neptune in the 1980s.
Reaching this third zone of our solar system – beyond the inner, rocky planets and outer gas giants – has been a space science priority for years. In the early 2000s the National Academy of Sciences ranked the exploration of the Kuiper Belt – and particularly Pluto and its largest moon, Charon – as its top priority planetary mission for the coming decade.
New Horizons – a compact, lightweight, powerfully equipped probe packing the most advanced suite of cameras and spectrometers ever sent on a first reconnaissance mission – is NASA’s answer to that call. “This is pure exploration; we’re going to turn points of light into a planet and a system of moons before your eyes!” said Alan Stern, New Horizons principal investigator from Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) in Boulder, Colorado. “New Horizons is flying to Pluto – the biggest, brightest and most complex of the dwarf planets in the Kuiper Belt. This 21st century encounter is going to be an exploration bonanza unparalleled in anticipation since the storied missions of Voyager in the 1980s.”
Pluto, the largest known body in the Kuiper Belt, offers a nitrogen atmosphere, complex seasons, distinct surface markings, an ice-rock interior that may harbor an ocean, and at least five moons. Among these moons, the largest – Charon - may itself sport an atmosphere or an interior ocean, and possibly even evidence of recent surface activity. “There’s no doubt, Charon is a rising star in terms of scientific interest, and we can’t wait to reveal it in detail in July,” said Leslie Young, deputy project scientist at SwRI.

Pluto’s smaller moons also are likely to present scientific opportunities. When New Horizons was started in 2001, it was a mission to just Pluto and Charon, before the four smaller moons were discovered.
The spacecraft’s suite of seven science instruments – which includes cameras, spectrometers, and plasma and dust detectors – will map the geology of Pluto and Charon and map their surface compositions and temperatures; examine Pluto’s atmosphere, and search for an atmosphere around Charon; study Pluto’s smaller satellites; and look for rings and additional satellites around Pluto.
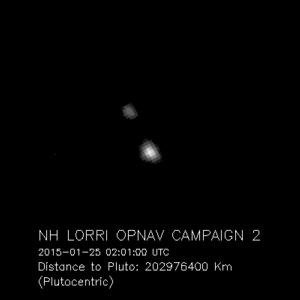
Currently, even with New Horizons closer to Pluto than the Earth is to the Sun, the Pluto system resembles little more than bright dots in the distance. But teams operating the spacecraft are using these views to refine their knowledge of Pluto’s location, and skillfully navigate New Horizons toward a precise target point 7,750 miles from Pluto’s surface. That targeting is critical, since the computer commands that will orient the spacecraft and point its science instruments are based on knowing the exact time and location that New Horizons passes Pluto.
“Our team has worked hard to get to this point, and we know we have just one shot to make this work,” said Alice Bowman, New Horizons mission operations manager at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, which built and operates the spacecraft. “We’ve plotted out each step of the Pluto encounter, practiced it over and over, and we’re excited the ‘real deal’ is finally here.”
The spacecraft’s work doesn’t end with the July flyby. Because it gets one shot at its target, New Horizons is designed to gather as much data as it can, as quickly as it can, taking about 100 times as much data on close approach as it can send home before flying away. And although the spacecraft will send select, high-priority datasets home in the days just before and after close approach, the mission will continue returning the data stored in onboard memory for a full 16 months. “New Horizons is one of the great explorations of our time,” said New Horizons Project Scientist Hal Weaver at APL. “There’s so much we don’t know, not just about Pluto, but other worlds like it. We’re not rewriting textbooks with this historic mission – we’ll be writing them from scratch.”
(Image from file)
 ANN FAQ: How Do I Become A News Spy?
ANN FAQ: How Do I Become A News Spy? Aero-News: Quote of the Day (10.28.25)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (10.28.25) ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (10.28.25)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (10.28.25) NTSB Final Report: Aviat Aircraft Inc A-1B
NTSB Final Report: Aviat Aircraft Inc A-1B ANN's Daily Aero-Term (10.28.25): Hold For Release
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (10.28.25): Hold For Release




