Common ARTS And Micro-EARTS Providing Controllers Data From
Both ADS-B And Radar
Multiple air traffic management platforms have been enhanced by
Lockheed Martin, enabling the processing of data received from
satellite-based navigational aids such as Automatic Dependent
Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B).
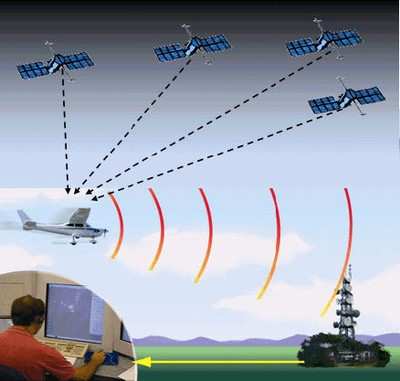
A key foundation of the FAA's Next Generation Air Transportation
System, ADS-B enables the transition from ground-based to
satellite-based air traffic control. This new infrastructure is set
to give pilots, as well as controllers, better information on the
position of the aircraft mid flight and on the airport surface.
The upgrades, made to the Microprocessor En Route Automated
Tracking System (Micro-EARTS) and Common Automated Radar Terminal
System (ARTS), along with enhancements made by the FAA to the Host
system in Houston, are helping to improve situational awareness
between pilots and air traffic controllers in Alaska, Louisville,
KY, and the Gulf of Mexico. The upgrades are part of the task
orders defined in the ADS-B Segment 1 schedule by the FAA's
Surveillance and Broadcast Services (SBS) office.
 Each upgraded system combines surveillance reports from
multiple sensors, including traditional radars and ADS-B into a
single track. Resulting tracks give air traffic controllers
improved aircraft position and velocity estimates. As a result, air
traffic controllers in these regions literally have a better
picture of the airspace in use because satellite-based surveillance
data can be processed by Lockheed Martin navigational tracking
platforms primarily used in terminal air traffic control
environments.
Each upgraded system combines surveillance reports from
multiple sensors, including traditional radars and ADS-B into a
single track. Resulting tracks give air traffic controllers
improved aircraft position and velocity estimates. As a result, air
traffic controllers in these regions literally have a better
picture of the airspace in use because satellite-based surveillance
data can be processed by Lockheed Martin navigational tracking
platforms primarily used in terminal air traffic control
environments.
"By completing these platform upgrades, our NextGen team is
helping pilots and controllers gain better situational awareness in
airspace over open water, such as the Gulf of Mexico, and
mountainous terrain, such as Alaska, where weather conditions can
change rapidly," said Mike Marsili, director of Terminal, Surface,
Flight Services and Airline Solutions for Lockheed Martin.
"Enabling greater use of ADS-B technology as quickly as possible is
a significant step for the FAA, and we're proud to be part of this
vital NextGen solution."
 When the FAA declared initial operating capability (IOC) at
the Anchorage Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) in late
April, it allowed the use of ADS-B for air traffic separation
services in Juneau, Alaska, via Micro-EARTS, and enhanced the ADS-B
coverage the FAA initiated in Alaska under the Capstone Project
five years ago.
When the FAA declared initial operating capability (IOC) at
the Anchorage Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) in late
April, it allowed the use of ADS-B for air traffic separation
services in Juneau, Alaska, via Micro-EARTS, and enhanced the ADS-B
coverage the FAA initiated in Alaska under the Capstone Project
five years ago.
"Our Micro-EARTS work in Alaska represents the final IOC defined
for air traffic control systems by the SBS office and successfully
demonstrates the integration of ADS-B data," noted Richard Nonini,
Lockheed Martin's director of Terminal and Surface Solutions.
 Upgrading Common ARTS was part of the initial ADS-B Segment 1
task order work at the FAA's Terminal Radar Approach Control
(TRACON) facility in Louisville, which achieved the initial ADS-B
IOC in November 2009. "Our Common ARTS work in Louisville was the
first FAA facility to use fused ADS-B track data for aircraft
surveillance in a fully operational air traffic control situation,"
Nonini said.
Upgrading Common ARTS was part of the initial ADS-B Segment 1
task order work at the FAA's Terminal Radar Approach Control
(TRACON) facility in Louisville, which achieved the initial ADS-B
IOC in November 2009. "Our Common ARTS work in Louisville was the
first FAA facility to use fused ADS-B track data for aircraft
surveillance in a fully operational air traffic control situation,"
Nonini said.
According to the FAA, Louisville was chosen as a key site in
part because UPS voluntarily outfitted much of its fleet with ADS-B
avionics. The system is being used by controllers in the tower at
Louisville International Airport and at the Louisville Terminal
Radar Approach Control (TRACON) facility.
The Louisville Common ARTS milestone on November 19, 2009, was
followed by an FAA-led change to the Host en route automation
system in Houston covering the Gulf of Mexico in December 2009, and
the Micro-EARTS improvements in Alaska achieving IOC April 28.
ADS-B is expected to be available nationwide by 2013.
 NTSB Final Report: Patriot Aircraft LLC CX1900A
NTSB Final Report: Patriot Aircraft LLC CX1900A Aero-News: Quote of the Day (12.06.25)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (12.06.25) ANN's Daily Aero-Term (12.06.25): High Speed Taxiway
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (12.06.25): High Speed Taxiway ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (12.06.25)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (12.06.25) Airborne-NextGen 12.02.25: Honda eVTOL, Arctus High-Alt UAS, Samson Patent
Airborne-NextGen 12.02.25: Honda eVTOL, Arctus High-Alt UAS, Samson Patent






