Thu, Sep 19, 2013
Spitzer Telescope Detected 'Comet Activity' From Don Quixote
For 30 years, a large near-Earth asteroid wandered its lone, intrepid path, passing before the scrutinizing eyes of scientists armed with telescopes while keeping something to itself. The object, known as Don Quixote, whose journey stretches to the orbit of Jupiter, now appears to be a comet. The discovery resulted from an ongoing project coordinated by researchers at Northern Arizona University, Flagstaff, AZ, using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. Through a lot of focused attention and a little luck, they found evidence of comet activity, which had evaded detection for three decades.
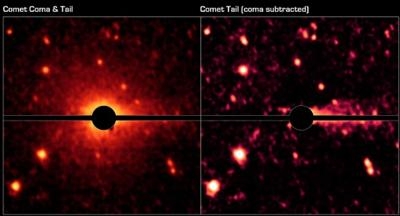
The results show that Don Quixote is not, in fact, a dead comet, as previously believed, but it has a faint coma and tail. In fact, this object, the third-biggest near-Earth asteroid known, skirts Earth with an erratic, extended orbit and is “sopping wet,” said David Trilling of Northern Arizona University, with large deposits of carbon dioxide and presumably water ice. Don Quixote is about 11 miles long. “This discovery of carbon dioxide emission from Don Quixote required the sensitivity and infrared wavelengths of the Spitzer telescope and would not have been possible using telescopes on the ground,” said Michael Mommert, who conducted the research at the German Aerospace Center, Berlin, before moving to Northern Arizona University. This discovery implies that carbon dioxide and water ice might be present on other near-Earth asteroids, as well.
The implications have less to do with a potential impact, which is extremely unlikely in this case, and more with “the origins of water on Earth,” Trilling said. Impacts with comets like Don Quixote over geological time may be the source of at least some of it, and the amount on Don Quixote represents about 100 billion tons of water -- roughly the same amount that can be found in Lake Tahoe, CA.
Mommert presented the results at the European Planetary Science Congress in London on Sept. 10.
(Image provided by NASA)
More News
From 2023 (YouTube Version): Legacy of a Titan Robert (Bob) Anderson Hoover was a fighter pilot, test pilot, flight instructor, and air show superstar. More so, Bob Hoover was an i>[...]
Get The Latest in Aviation News NOW on Instagram Are you on Instagram yet? It's been around for a few years, quietly picking up traction mostly thanks to everybody's new obsession >[...]
Aero Linx: B-52H Stratofortress The B-52H Stratofortress is a long-range, heavy bomber that can perform a variety of missions. The bomber is capable of flying at high subsonic spee>[...]
Altimeter Setting The barometric pressure reading used to adjust a pressure altimeter for variations in existing atmospheric pressure or to the standard altimeter setting (29.92).>[...]
"Knowing that we play an active part in bettering people's lives is extremely rewarding. My team and I are very thankful for the opportunity to be here and to help in any way we ca>[...]
 Classic Aero-TV: Remembering Bob Hoover
Classic Aero-TV: Remembering Bob Hoover ANN FAQ: Follow Us On Instagram!
ANN FAQ: Follow Us On Instagram! ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.15.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.15.24) ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.15.24):Altimeter Setting
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.15.24):Altimeter Setting Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.16.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.16.24)



