Walking A Challenge After A Long Space Mission
 Astronauts returning from
challenging long-duration missions face one more challenge when
they get back to Earth -- standing up and walking.
Astronauts returning from
challenging long-duration missions face one more challenge when
they get back to Earth -- standing up and walking.
Upon returning to normal gravity, astronauts often suffer from
balance problems that lead to dizziness and difficulty standing,
walking and turning corners. Dr. Jacob Bloomberg is leading a group
of National Space Biomedical Research Institute (NSBRI) scientists
in a project to develop techniques to help astronauts adapt quickly
to a new gravity environment and to overcome balance disturbances.
This concept will also have benefits for non-astronaut populations
such as the elderly or people with balance disorders.
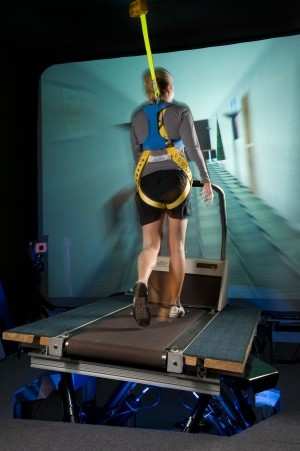
Bloomberg of NASA Johnson Space Center Neurosciences Laboratory
and his colleagues use a system that consists of a treadmill
mounted on a base that can be actively moved in different
directions to simulate balance disturbances. Called an Adaptability
Training System, the treadmill has a projection screen in front of
it that shows an image of a room or hallway that moves as the user
walks. Disturbances are simulated by tilting the treadmill in one
direction as the image is tilted in another.
"At first, people find it difficult to walk on the treadmill
since its movement and images are out of sync. But over time, they
learn to walk on it efficiently. We call this concept 'learning to
learn,'" said Bloomberg, who is the associate team leader of
NSBRI's Sensorimotor Adaptation Team and a senior research
scientist at NASA.
In order to perform everyday activities, the brain interprets
information provided by the body's sensory systems: the eyes, the
inner ear balance organs, the skin and muscle movement receptors.
Bloomberg said the problems for astronauts occur during the
transition period in which the brain is trying to adapt to a new
gravity environment -- either returning to Earth or in the future
adjusting to lunar or martian gravity.
"In space, information from the sensory systems is different,
particularly when you take away gravity. The brain reinterprets
that information, makes adjustments and allows you to do the
activities you need to do in space," Bloomberg said. "The down side
to that is when you return to Earth, the sensory systems are not
used to a normal gravity environment."
Former NASA astronaut Dr. Leroy Chiao experienced balance
disturbances following his four spaceflights, one of which was a
six-month stay on the International Space Station (ISS). He
compared the effects to those experienced after stepping off a
fast-spinning playground merry-go-round. "After a merry-go-round
ride, the effects go away pretty quickly," Chiao said. "But after a
spaceflight, they linger."
Post-flight data collected indicates a correlation between the
length of the mission and how long effects linger. Bloomberg said
if an astronaut has been in space on a typical two-week shuttle
mission, it may take several days to recover. For six-month stays
aboard the ISS, it could take at least several weeks to return to
normal.

In addition to maximizing training efficiency, Bloomberg is
looking at how long the benefit of the adaptability training lasts.
Once subjects master the treadmill, they come back periodically for
testing to see how well they perform. He is investigating if
subjects can retain the training for up to six months, which would
allow the training to take place before a long space mission.
An eventual goal of the researchers is to integrate a version of
the system into the treadmill on a spacecraft, allowing astronauts
to perform adaptability training on long missions. Integration
would save space and power, both precious commodities on a
spacecraft.
NSBRI, funded by NASA, is a consortium of institutions studying
the health risks related to long-duration spaceflight. The
Institute's science, technology and education projects take place
at more than 60 institutions across the United States.
 Bolen Gives Congress a Rare Thumbs-Up
Bolen Gives Congress a Rare Thumbs-Up The SportPlane Resource Guide RETURNS!!!!
The SportPlane Resource Guide RETURNS!!!! Buying Sprees Continue: Textron eAviation Takes On Amazilia Aerospace
Buying Sprees Continue: Textron eAviation Takes On Amazilia Aerospace Hawker 4000 Bizjets Gain Nav System, Data Link STC
Hawker 4000 Bizjets Gain Nav System, Data Link STC Echodyne Gets BVLOS Waiver for AiRanger Aircraft
Echodyne Gets BVLOS Waiver for AiRanger Aircraft





