The NTSB Issued A Total Of Four Safety Recommendations To The FAA
The NTSB determined during a public meeting Tuesday, a pilot’s decision to continue flight under visual flight rules into instrument meteorological conditions, which resulted in the pilot’s spatial disorientation and loss of control, led to the fatal, Jan. 26, 2020, crash of a Sikorsky S-76B helicopter in Calabasas, California.

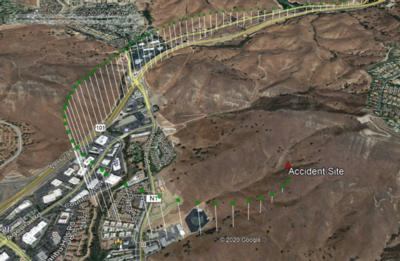
The pilot and eight passengers died when the helicopter, operated by Island Express Helicopters, Inc., entered a rapidly descending left turn and crashed into terrain. The flight departed from John Wayne Airport-Orange County, Santa Ana, California, and was bound for Camarillo, California.
About two minutes before the crash, while at an altitude of about 450 feet above ground level, the pilot transmitted to an air traffic control facility that he was initiating a climb to get the helicopter “above the [cloud] layers.” The helicopter climbed at a rate of about 1,500 feet per minute and began a gradual left turn. The helicopter reached an altitude of about 2,400 feet above sea level (1,600 feet above ground level) and began to descend rapidly in a left turn to the ground. While the helicopter was descending the air traffic controller asked the pilot to “say intentions,” and the pilot replied that the flight was climbing to 4,000 feet msl (about 3,200 feet above ground level). A witness first heard the helicopter and then saw it emerge from the bottom of the cloud layer in a left-banked descent about one or two seconds before impact.
Contributing to the accident was the pilot’s likely self-induced pressure and plan continuation bias, which adversely affected his decision making. The NTSB also determined Island Express Helicopters Inc.’s inadequate review and oversight of its safety management process contributed to the crash.
“Unfortunately, we continue to see these same issues influence poor decision making among otherwise experienced pilots in aviation crashes,” said NTSB Chairman Robert Sumwalt. “Had this pilot not succumbed to the pressures he placed on himself to continue the flight into adverse weather, it is likely this accident would not have happened. A robust safety management system can help operators like Island Express provide the support their pilots need to help them resist such very real pressures.”
The report discussed during Tuesday’s meeting highlighted Island Express Helicopters Inc.’s inadequate review and oversight of its safety management processes. Island Express Helicopters Inc.’s lack of a documented policy and safety assurance evaluations to ensure its pilots were consistently and correctly completing the flight risk analysis forms, hindered the effectiveness of the form as a risk management tool.
The NTSB concluded a fully implemented, mandatory safety management system could enhance Island Express Helicopter Inc.’s ability to manage risks.
Based upon its investigation the NTSB issued a total of four safety recommendations to the Federal Aviation Administration and to IslandExpress Helicopters Inc. These recommendations address safety issues including preflight weather and flight risk planning, spatial disorientation, inflight decision-making, the benefits of a mandatory safety management system, and the benefits of a flight data monitoring program.
 NTSB Final Report: Douglas A-4K
NTSB Final Report: Douglas A-4K ANN FAQ: Q&A 101
ANN FAQ: Q&A 101 Classic Aero-TV: PBY Catalina--From Wartime to Double Sunrise to the Long Sunset
Classic Aero-TV: PBY Catalina--From Wartime to Double Sunrise to the Long Sunset ANN's Daily Aero-Term (07.01.25): Advanced Air Mobility (AAM)
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (07.01.25): Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (07.01.25)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (07.01.25)





