Wed, Oct 12, 2022
T901 Shaping Up to Offer 50% Power Bump with 25% Better Fuel Burn
GE Aerospace is on track for next year's T-901 testing program, getting ready to put the next-generation rotorcraft engine through its paces for installation in a range of combat helicopters.
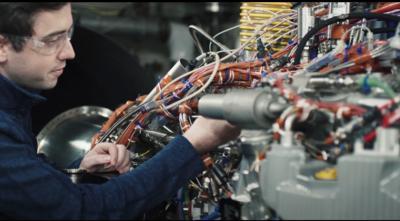
The T901-GE-900 will ultimately power the US Army's UH-60 Black Hawk, the AH-64 Apache, and the upcoming Future Attack Reconnaissance Aircraft (FARA) once ready for duty. The testing process is part of the Engineering and Manufacturing Development (EMD) phase of the Army’s Improved Turbine Engine (ITE) program. Once complete, the program is expected to offer a substantive leap in reliability and performance, boosting performance and minimizing downtime for combat aircraft.
Key to the improvements over legacy engine systems is the simplification of parts made possible through modern additive manufacturing. The rapid advancement of industrial scale 3d printing allows considerable reductions in machining and forging smaller parts, reducing failure points and combining processes for greater resiliency throughout the life of the unit. Combined with a series of modern materials, the resulting engine is proving to be an impressive upgrade over the Army's current helicopter workhorse, the GE T700. The T901 provides 50% more power over its older counterpart, putting out 3,000 shaft horsepower. Army personnel undoubtedly eye the program with excitement at the prospect of once again having their aircraft's full payload capacity even in hot and high climates. Like any modern upgrade, the performance boost comes alongside improvements in fuel consumption, with the T901 boasting 25% greater fuel economy in flight.

“Testing of the first T901 engine was very successful with the engine accumulating more than 100 hours of run time,” said Tom Champion, GE’s T901 Program Director. “We were impressed with the performance and condition of the engine’s compressor, combustor, and turbine sections as well as the 3D-printed (additive) manufactured parts and ceramic matrix composite (CMC) components.”
Under the program, 8 initial T901 engines will be built as a part of the Army's airworthiness certification program, ultimately logging thousands of hours and testing on each before giving them the go-ahead for combat use. So far, the first T901 unit has been put through 1,500 hours of full-scale ground testing for its preliminary flight rating, with nearly 5,000 hours of engine qualification testing, with many more well on the way.
More News
"The owners envisioned something modern and distinctive, yet deeply meaningful. We collaborated closely to refine the flag design so it complemented the aircraft’s contours w>[...]
Nonradar Arrival An aircraft arriving at an airport without radar service or at an airport served by a radar facility and radar contact has not been established or has been termina>[...]
From 2022 (YouTube Edition): Still Life with Verve David Uhl was born into a family of engineers and artists—a backdrop conducive to his gleaning a keen appreciation for the >[...]
Also: Electra Goes Military, Miami Air Taxi, Hypersonics Lab, MagniX HeliStrom Amazon’s Prime Air drones are back in the spotlight after one of its newest MK30 delivery drone>[...]
Also: Trailblazing Aviator Betty Stewart, Wind Farm Scrutiny, Chatham Ban Overturned, Airbus Shares Dive A Thunderbird pilot, ID'ed alternately as Thunderbird 5 or Thunderbird 6, (>[...]
 Aero-News: Quote of the Day (12.11.25)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (12.11.25) ANN's Daily Aero-Term (12.11.25): Nonradar Arrival
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (12.11.25): Nonradar Arrival Classic Aero-TV: David Uhl and the Lofty Art of Aircraft Portraiture
Classic Aero-TV: David Uhl and the Lofty Art of Aircraft Portraiture Airborne-NextGen 12.09.25: Amazon Crash, China Rocket Accident, UAV Black Hawk
Airborne-NextGen 12.09.25: Amazon Crash, China Rocket Accident, UAV Black Hawk Airborne 12.05.25: Thunderbird Ejects, Lost Air india 737, Dynon Update
Airborne 12.05.25: Thunderbird Ejects, Lost Air india 737, Dynon Update




