Sat, Jan 03, 2015
Software Simulates Arriving And Departing Traffic To Assist In Runway Assignments And Sequencing
For several years, the FAA has used the results of an airport capacity tool called the runwaySimulator model that was developed by MITRE to efficiently evaluate an airport’s capacity.
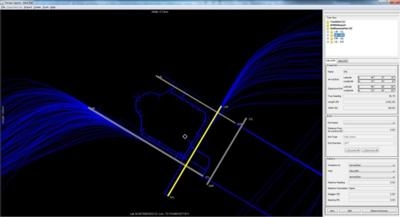
The tool is now being made publicly available to those with interests in aviation and airport planning. The tool can be used to assess an airport’s existing capacity, as well as capacity improvements with new infrastructure or flight procedures.
The runwaySimulator model simulates arriving and departing traffic at an airport, the decisions made about runway assignment and sequencing, and the flight operations themselves. The model generates a randomized traffic sample that keeps pressure on the airport. The traffic sample reflects an airport's mix of aircraft types, which differ in their performance parameters.
FAA separation standards are codified in the software as rules that govern pairs of flight operations, and these are modified to represent common pilot and controller behaviors. The runway configuration is set and exceptions noted to prohibit use of specified runways by certain aircraft types or to set aside runways for exclusive use by, say, general aviation traffic. A heuristic algorithm assigns runways and sequences traffic to balance efficiency and delay while respecting separation requirements and runway eligibilities.
When used to estimate capacity, runwaySimulator generates traffic so there is constant demand on the runway system. It does this for various arrival-departure mixes and, for each, simulates steady-state operations for several hundred hours. The average throughput achieved is recorded for each arrival-departure mix and used to create the airport's capacity "curve" (i.e., a Pareto frontier). The model provides a variety of measurements and visualizations to the analyst to verify and validate the simulation.
The tool can be used to estimate runway capacity with current and future operations. However, runwaySimulator does not evaluate most non-runway constraints at the airport nor limitations elsewhere in the national airspace system. Such constraints may include taxiway or gate constrains, terminal airspace congestion, Air Traffic Control traffic management initiatives, and seasonal limitations due to high temperatures that restrict aircraft climb rates.
(Runway simulator screenshot provided by the FAA)
More News
Aero Linx: Transport Canada We are a federal institution, leading the Transport Canada portfolio and working with our partners. Transport Canada is responsible for transportation p>[...]
Gross Navigation Error (GNE) A lateral deviation from a cleared track, normally in excess of 25 Nautical Miles (NM). More stringent standards (for example, 10NM in some parts of th>[...]
From AirVenture 2017 (YouTube Edition): Flight-Proven Booster On Display At AirVenture… EAA AirVenture Oshkosh is known primarily as a celebration of experimental and amateu>[...]
Aircraft Parachute System (CAPS) Was Deployed About 293 Ft Above Ground Level, Which Was Too Low To Allow For Full Deployment Of The Parachute System Analysis: The day before the a>[...]
Also: 48th Annual Air Race Classic, Hot Air Balloon Fire, FAA v Banning 100LL, Complete Remote Pilot The news Piper PA-18 Super Cub owners have been waiting for has finally arrived>[...]
 ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (06.29.25)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (06.29.25) ANN's Daily Aero-Term (06.29.25): Gross Navigation Error (GNE)
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (06.29.25): Gross Navigation Error (GNE) Classic Aero-TV: Anticipating Futurespace - Blue Origin Visits Airventure 2017
Classic Aero-TV: Anticipating Futurespace - Blue Origin Visits Airventure 2017 NTSB Final Report: Cirrus SR22
NTSB Final Report: Cirrus SR22 Airborne Affordable Flyers 06.26.25: PA18 Upgrades, Delta Force, Rhinebeck
Airborne Affordable Flyers 06.26.25: PA18 Upgrades, Delta Force, Rhinebeck



