Wed, Jun 06, 2018
Misidentification Of Runway In Reduced Visibility Contributed To The March 2017 Risk Of Collision With Terrain Of A WestJet Flight
In its investigation report (A17F0052) released Monday, the Transportation Safety Board of Canada (TSB) found that unexpected weather conditions on final approach, reduced runway conspicuity, and inadequate flight path monitoring led to a risk of collision with terrain.
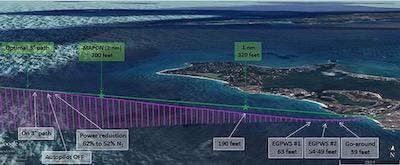
On March 7, 2017, a WestJet Boeing 737-800 was operating as flight 2652 from Toronto/Lester B. Pearson International Airport (CYYZ), Ontario, to Princess Juliana International Airport (TNCM) in Sint Maarten with 158 passengers and six crew members on board. It entered a significant rain shower shortly after crossing the MAPON (missed approach point) waypoint. The crew initiated a missed approach 0.30 nautical miles from the runway threshold at an altitude of 40 feet above water. Once visibility improved, the crew conducted a second approach and landed without incident.
The investigation determined that the runway lights and the visual guidance system (PAPI) had been set at a low intensity during the rain shower that had obscured the view of the airport environment. Both the shower and the low lighting limited the visual references available to the crew to identify the runway properly until the aircraft had exited the rain shower and visibility sharply improved.
The sudden and unexpected poor visibility during the final approach increased the flight crew's visual workload and led to inadequate altitude monitoring. The crew did not notice that the aircraft had descended below the normal angle of descent to the runway threshold until the enhanced ground proximity warning system issued an alert.
After the occurrence, WestJet developed a corrective action plan, including information for pilots regarding possible challenges and threats on approaching and landing at Princess Juliana International Airport. WestJet also revised its Route & Aerodrome Qualification for TNCM with additional information. In addition, guidance on airport lighting system management will be added to the Air Traffic Services operations manual in TNCM by September 2018.
The TSB is an independent agency that investigates marine, pipeline, railway and aviation transportation occurrences. Its sole aim is the advancement of transportation safety. It is not the function of the Board to assign fault or determine civil or criminal liability.
(Source: TSB Canada news release. Image from TSB Canada report)
More News
From 2014 (YouTube Version): One Of The Airshow World's Pre-Eminent Formation Teams Chats About The State Of The Industry At EAA AirVenture 2014, ANN News Editor Tom Patton gets th>[...]
Tactical Air Navigation (TACAN) An ultra-high frequency electronic rho-theta air navigation aid which provides suitably equipped aircraft a continuous indication of bearing and dis>[...]
Aero Linx: Doobert Hi, we're Chris & Rachael Roy, founders and owners of Doobert. Chris is a technology guy in his “day” job and used his experience to create Doobe>[...]
The Airplane Was Spinning In A Nose-Down Attitude Before It Impacted Terrain On June 20, 2025, at 0900 eastern daylight time, a Pitts Aerobatics S-2B, N79AV, was destroyed when it >[...]
Also: United Elite Sues, Newark ATC Transitions, Discovery Moves?, Textron @ KOSH The Commemorative Air Force Airbase Arizona is taking its “Flying Legends of Victory Tour&rd>[...]
 Classic Aero-TV: Up Close And Personal - The Aeroshell Aerobatic Team at Oshkosh
Classic Aero-TV: Up Close And Personal - The Aeroshell Aerobatic Team at Oshkosh ANN's Daily Aero-Term (07.13.25): Tactical Air Navigation (TACAN)
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (07.13.25): Tactical Air Navigation (TACAN) ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (07.13.25)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (07.13.25) NTSB Prelim: Pitts S2
NTSB Prelim: Pitts S2 Airborne 07.09.25: B-17 Sentimental Journey, Airport Scandal, NORAD Intercepts
Airborne 07.09.25: B-17 Sentimental Journey, Airport Scandal, NORAD Intercepts



