Spacecraft Launched On December 3 Now In Working Orbit
The two cubes housed in the core of ESA’s LISA Pathfinder were left to move under the effect of gravity alone earlier this week – another milestone towards demonstrating technologies to observe gravitational waves from space.

It has been an intense couple of months for LISA Pathfinder. After launch on 3 December and six burns to raise the orbit, it finally reached its work site just under 1 million miles from Earth towards the Sun in January, and the team of engineers and scientists started to switch on and test its systems.
One of the most delicate operations entailed releasing the two test masses from the mechanisms that kept them in place during ground handling, launch and cruise.
First, the eight locking ‘fingers’ pressing on the corners of the identical gold–platinum cubes were retracted on 3 February. The cubes were then being held in position only by two rods, softly pushing on opposite faces.
These rods were retracted from the first test mass on 15 February, and from the second on the following day, leaving the cubes floating freely several millimetres from the walls of their housings.
Over the following days, minute electrostatic forces were applied to maneuvre the cubes and make them track the spacecraft’s motion through space as it is slightly disturbed by external forces such as the pressure from sunlight.
This enabled the team to run further tests on the instruments, including the system used to measure the electrical charge of each cube and the procedures used to monitor their position and orientation.
Then the team aligned the two cubes with the laser beams that link them, and checked that the laser measurements agreed with those from the electrostatic sensors.
After verifying that everything was working as planned, the intensity of the electrostatic forces was gradually reduced until none was being applied along the sensitive axes of the masses. This resulted in a brief test of drag-free motion, on 19 February.
Finally, on 22 February, the team tackled the greatest challenge: setting the two cubes completely free, letting them move under the effect of gravity alone and actively manoeuvring the spacecraft around them.
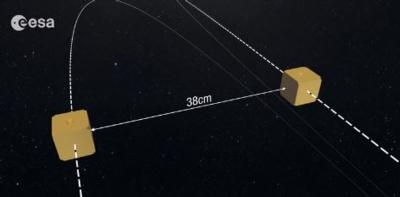
To do this, LISA Pathfinder measures the position and orientation of each cube, and corrects its movement by firing microthrusters to keep it centred on one cube.
“This is a historic achievement: we are demonstrating the most precise freefall that has ever been obtained in space,” says Paul McNamara, LISA Pathfinder project scientist.
On 23 February, the spacecraft’s main operating mode was switched on for the first time. With the test masses in freefall, all of the key elements are now in place to start LISA Pathfinder’s scientific mission on 1 March, following some final tests on the fully operational payload in the coming days.
Reproducing a motion as close as possible to actual freefall is the challenging condition needed to build and operate future space missions to observe gravitational waves.
Albert Einstein predicted the existence of gravitational waves, fluctuations in the fabric of spacetime, a century ago and they were recently directly detected with the ground-based Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), as announced on 11 February.
Space and ground experiments are sensitive to different sources of gravitational waves, so future space missions will be key partners to ground facilities such as LIGO, the European Gravitational Observatory and the Virgo Collaboration, which are already active in this quest.
A spaceborne gravitational wave observatory was identified as the goal for the L3 mission in ESA’s Cosmic Vision programme, and LISA Pathfinder will lay the foundations for these future investigations of the gravitational Universe.
“It is an immense reward to see this pioneering spacecraft ready to start its crucial mission,” concludes César García Marirrodriga, ESA’s project manager.
(Image provided with ESA news release)
 ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.02.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (05.02.24) ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.02.24): Touchdown Zone Lighting
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (05.02.24): Touchdown Zone Lighting Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.02.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (05.02.24) ANN FAQ: Contributing To Aero-TV
ANN FAQ: Contributing To Aero-TV NTSB Final Report: Cirrus Design Corp SR20
NTSB Final Report: Cirrus Design Corp SR20




