Cassini-Huygens Mission Makes Molecular Discovery
The international Cassini-Huygens mission has made a surprising detection of a molecule that is instrumental in the production of complex organics within the hazy atmosphere of Saturn’s moon Titan.
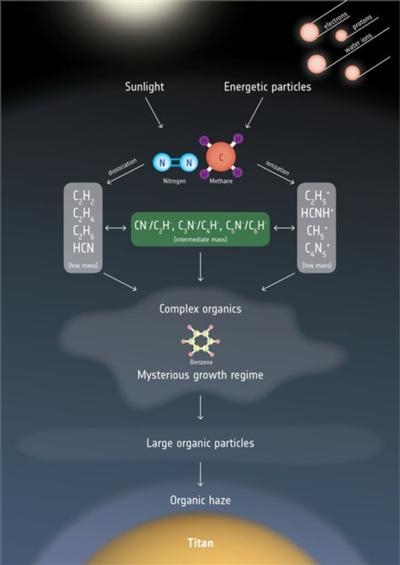
Titan boasts a thick nitrogen and methane atmosphere with some of the most complex chemistry seen in the Solar System. It is even thought to mimic the atmosphere of early Earth, before the build-up of oxygen. As such, Titan can be seen as a planet-scale laboratory that can be studied to understand the chemical reactions that may have led to life on Earth, and that could be occurring on planets around other stars.
In Titan’s upper atmosphere, nitrogen and methane are exposed to energy from sunlight and energetic particles in Saturn’s magnetosphere. These energy sources drive reactions involving nitrogen, hydrogen and carbon, which lead to more complicated prebiotic compounds.
These large molecules drift down towards the lower atmosphere, forming a thick haze of organic aerosols, and are thought to eventually reach the surface. But the process by which simple molecules in the upper atmosphere are transformed into the complex organic haze at lower altitudes is complicated and difficult to determine.
One surprising outcome of the Cassini mission was the discovery of a particular type of negatively charged molecule at Titan. Negatively charged species – or ‘anions’ – were not something scientists expected to find, because they are highly reactive and should not last long in Titan’s atmosphere before combining with other materials. Their detection is completely reshaping current understanding of the hazy moon’s atmosphere.
In a new study published in Astrophysical Journal Letters, scientists identified some of the negatively charged species as what are known as ‘carbon chain anions’. These linear molecules are understood to be building blocks towards more complex molecules, and may have acted as the basis for the earliest forms of life on Earth.
The detections were made using Cassini’s plasma spectrometer, called CAPS, as Cassini flew through Titan’s upper atmosphere, 950–1300 km above the surface. Interestingly, the data showed that the carbon chains became depleted closer to the moon, while precursors to larger aerosol molecules underwent rapid growth, suggesting a close relationship between the two, with the chains ‘seeding’ the larger molecules.
“We have made the first unambiguous identification of carbon chain anions in a planet-like atmosphere, which we believe are a vital stepping-stone in the production line of growing bigger, and more complex organic molecules, such as the moon’s large haze particles,” says Ravi Desai of University College London and lead author of the study. “This is a known process in the interstellar medium, but now we’ve seen it in a completely different environment, meaning it could represent a universal process for producing complex organic molecules. The question is, could it also be happening within other nitrogen-methane atmospheres like at Pluto or Triton, or at exoplanets with similar properties?"
"The prospect of a universal pathway towards the ingredients for life has implications for what we should look for in the search for life in the Universe,” says co-author Andrew Coates, also from UCL, and co-investigator of CAPS. “Titan presents a local example of exciting and exotic chemistry, from which we have much to learn.”
Cassini’s 13-year odyssey in the Saturnian system will soon draw to a close, but future missions, such as the international James Webb Space Telescope and ESA’s Plato exoplanet mission are being equipped to look for this process not only in our own Solar System but elsewhere. Advanced ground-based facilities such as ALMA could also enable follow-up observations of this process at work in Titan’s atmosphere, from Earth.
“These inspiring results from Cassini show the importance of tracing the journey from small to large chemical species in order to understand how complex organic molecules are produced in an early Earth-like atmosphere,” adds Nicolas Altobelli, ESA’s Cassini–Huygens project scientist.
“While we haven’t detected life itself, finding complex organics not just at Titan, but also in comets and throughout the interstellar medium, we are certainly coming close to finding its precursors.”
(Image provided with ESA news release)
 ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.28.24): Airport Marking Aids
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.28.24): Airport Marking Aids Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.28.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.28.24) ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.28.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.28.24) Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.29.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.29.24) ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.29.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.29.24)



