Mon, Jan 14, 2013
Milky Way Galaxy May Contain 17 Billion Planets Of Similar Size
The quest to determine if planets like Earth are rare or common is taking another stride forward. Using NASA's Kepler spacecraft, managed by NASA Ames Research Center, astronomers are beginning to find Earth-sized planets orbiting distant stars. A new analysis of Kepler data shows that about 17 percent of stars have an Earth-sized planet in an orbit closer than Mercury. Since the Milky Way has about 100 billion stars, there are at least 17 billion Earth-sized worlds out there.
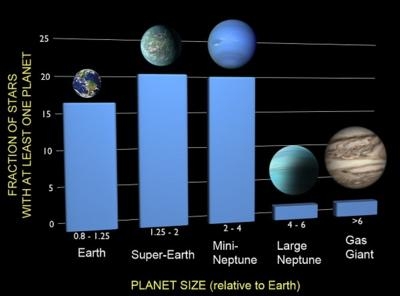
Francois Fressin, of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA), presented the analysis today in a press conference at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Long Beach, CA. A paper detailing the research has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. The research team found that 50 percent of all stars have a planet of Earth-size or larger in a close orbit. By adding larger planets detected in wider orbits up to the orbital distance of the Earth, this number increases to 70 percent.
Extrapolating from Kepler's currently ongoing observations and results from other detection techniques, scientists have determined that nearly all sun-like stars have planets. Planets closer to their stars are easier to find because they transit more frequently. As more data are gathered, planets in larger orbits will be detected. In particular, Kepler's extended mission will enable the detection of Earth-sized planets at greater distances, including Earth-like orbits in the "habitable zone," the region in a planetary system where liquid water might exist on the surface of an orbiting planet.
Kepler is the first NASA mission capable of finding Earth-size planets orbiting in or near the habitable zone of the host star. NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA, is the home organization of the science principal investigator, and is responsible for the ground system development, mission operations, and science data analysis.
(Image provided by NASA)
More News
Light Gun A handheld directional light signaling device which emits a brilliant narrow beam of white, green, or red light as selected by the tower controller. The color and type of>[...]
"The journey to this achievement started nearly a decade ago when a freshly commissioned Gentry, driven by a fascination with new technologies and a desire to contribute significan>[...]
Aero Linx: JAARS, Inc. For decades now, we’ve landed planes on narrow rivers and towering mountains. We’ve outfitted boats and vehicles to reach villages that rarely se>[...]
"Our driven and innovative team of military and civilian Airmen delivers combat power daily, ensuring our nation is ready today and tomorrow." Source: General Duke Richardson, AFMC>[...]
Aircraft Conflict Predicted conflict, within EDST of two aircraft, or between aircraft and airspace. A Red alert is used for conflicts when the predicted minimum separation is 5 na>[...]
 ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.20.24): Light Gun
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.20.24): Light Gun Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.20.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.20.24) ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.21.24)
ANN's Daily Aero-Linx (04.21.24) Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.21.24)
Aero-News: Quote of the Day (04.21.24) ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.21.24): Aircraft Conflict
ANN's Daily Aero-Term (04.21.24): Aircraft Conflict



